MultiChain is a fork of Bitcoin that is open source. It is simple to configure and may be used to launch bespoke blockchains, both private and public. It comes with a carefully chosen mix of features and upgrades aimed at corporate and commercial users. Support for native assets and bigger quantities of arbitrary data storage […]
Updated 12 February 2024

VP – Pre Sales at Appventurez
MultiChain is a fork of Bitcoin that is open source. It is simple to configure and may be used to launch bespoke blockchains, both private and public. It comes with a carefully chosen mix of features and upgrades aimed at corporate and commercial users. Support for native assets and bigger quantities of arbitrary data storage is promising.
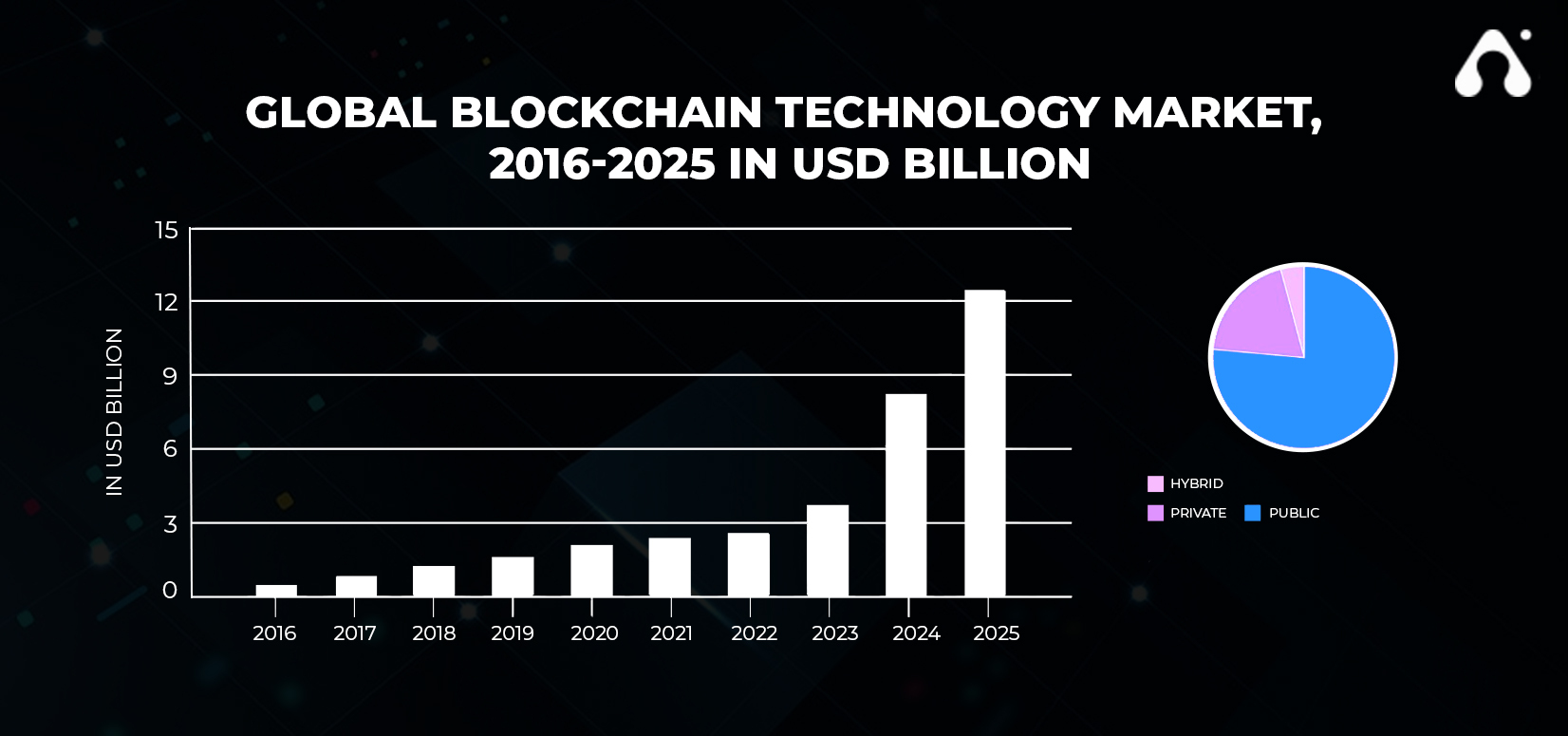
Some analysts predict that the blockchain sector will be worth more than $21 billion by 2025. The total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies has now surpassed $1.9 trillion. Governments, corporations, institutional investors, and people are all growing more enthusiastic about the developing industry, which was long distinguished by its tight-knit community and exclusivity.
For several years, blockchain has been the biggest subject on news channels, social media platforms, and workplace group conversations. And there’s no hint that the buzz surrounding multichain in blockchain and cryptocurrency will abate anytime soon.
The ascent of blockchain, accompanied by its myriad supporters and detractors, has propelled it into the spotlight of popularity. The proliferation of blockchain apps and development tools has contributed significantly to its widespread adoption. The term “blockchain” has become such a ubiquitous buzzword that even ordinary corporations, undergoing a transformation in name and business strategy to align with the blockchain craze, are experiencing a notable upswing in earnings. This fervor extends to the realm of blockchain app development services, where the demand for expertise in crafting decentralized solutions is witnessing a parallel surge.
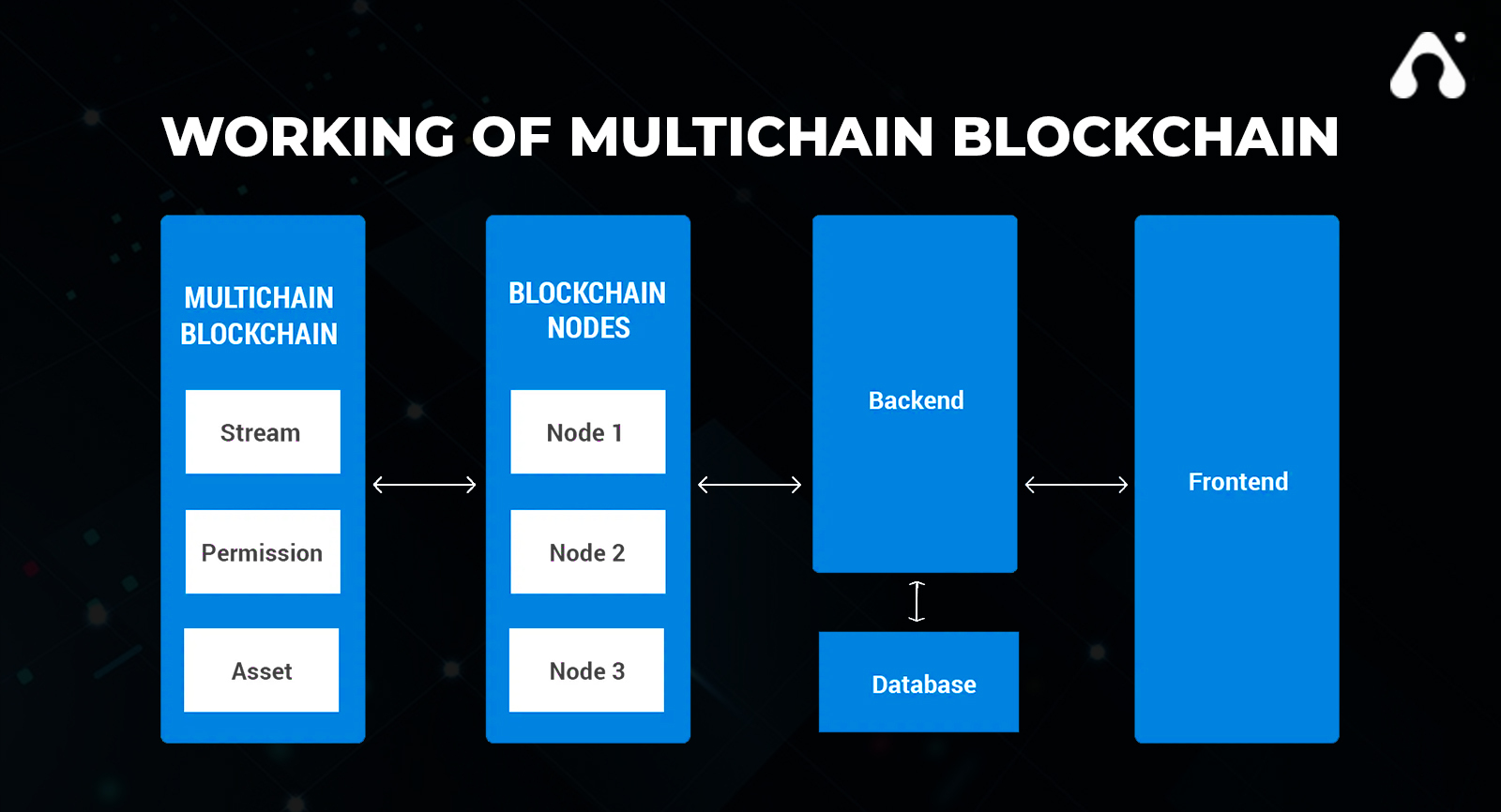
Multichain in blockchain is an open-source blockchain platform that was intended to generate blockchain applications that may function within or between organizations. Blockchain app development services are used for private use and may be used for financial transactions by businesses.
The multichain blockchain’s goal is to maintain transaction visibility purely amongst the chosen parties while still ensuring stability and control. With the support of proof of work and cost control, it makes the mining process more convenient.
Multichain features have a blockchain with a lightweight private network that is easy to create and manage, with developer-friendly and versatile tools. It also supports a variety of programming languages. Native tokens, which are the network’s assets, may be generated and transferred between users on the network.
The main objective of Multichain in blockchain is a ready-to-use network that mimics some of the features of Bitcoin to develop wallet apps. It does so by extending the Bitcoin API and platform, making it compatible with a wide range of Bitcoin-related applications and open-source platforms. Instead of being uniform, network nodes merely need to be linked. This effectively implies that all roles of multichain blockchain participating systems, whether inside one organization or between various organizations sharing the same transaction database, become part of a multichain blockchain network.
When two blockchain nodes link on a peer-to-peer network, this is known as multichain. Each node’s identity is represented by an address with a set of rights. As a consequence, each node sends messages to other users, and if they don’t get satisfactory responses, the peer-to-peer connection is terminated. Handshaking is the process of two nodes connecting to build a multichain in blockchain for business.
A distributed consensus approach is used to mine by a group of network administrators. Multichain blockchain platform identifies miners through an identifiable collection of entities, and a mining diversity criterion is implemented, with a value between 0 and 1. The following steps are taken to ensure that a block is effective.
The transaction fees and block rewards are almost nothing, and the miners’ reward is the blockchain understanding its basics and knowing how it works seamlessly. However, miners can be compensated in local currency in return for tokenized assets.
In multichain, network admins create rights to access the network, which are normally done by default by developers. The platform’s built-in capabilities enable developers to tailor the network to criteria such as mining diversity, consensus mechanism, mining payouts, access permissions, blockchain privacy, and so on. Permissions are granted and revised in multichain utilizing network transactions containing specified data.
Streams are private shared databases that may be used for data access, retrieval, time stamping, and archiving on the multichain blockchain network. Streams are collections of data objects with a timestamp, digital signature, and an optional key for accessing the data. The streams can be public, which means that anybody can write them. It can also be made private or only accessible to certain people.
Assets are the blockchain’s native tokens, and the multichain in blockchain enables the creation and tracking of native assets at the blockchain level. Every node in the blockchain confirms the total amount of assets.
The data storage mechanisms used by multichain blockchains are dual chains. That simply means that every piece of publicly available data can be on the chain or off the chain as desired. Unlike previous blockchains, the data is not copied across all nodes. Only those people who are supposed to see the dataset have access to the decryption key. Multichain in blockchain can now process up to 2,000 transactions per second.
When the nodes in a blockchain communicate with each other, the act of hand-shaking happens. Each node’s identity is represented by an address with a set of permissions. As a result, nodes transmit messages to each other, and if they do not receive satisfactory messages, the peer-to-peer (P2P) connection is terminated.
Miners for an identified group of entities are defined by the MultiChain. It adds the mining diversity criteria, which links 0= mining diversity = 1.
In the same way that different platforms have different programming languages, different programming languages may be considered while developing blockchain applications. You can start with top blockchain classic programming languages such as C++, Python, Go, and Java, or go on to the more complex role of multichain in blockchain-specific languages such as Simplicity and Solidity.
The creation of smart contracts on the blockchain is based on simplicity. The language is simple, leverages static analysis, and may be thought of as a step up from basic cryptocurrency languages such as Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Bitcoin Script.
Solidity is a statically typed blockchain programming language that is primarily used to create EVM-based smart contracts. With this language, self-regulating business logic may be simply implemented in smart contracts, leaving a non-repudiable and authoritative record of transactions.
Blockchain technology trends to help transform into a high-growth sector, it will be important to master the present blockchain complications.
Multichain is the future of blockchain that would facilitate blockchain adoption in a variety of industries, including finance and banking. Transactions between banks utilizing various blockchains would be extremely complicated if there was no such interoperability. However, with a multichain strategy, data transmission would be not only easy but also quick and secure.
Consider Ethereum and other big layer-one blockchains as a city. They are more crowded and pricey, yet they have some advantages. Layer-two blockchains and sidechains, on the other hand, are more like the suburbs. They are less crowded and may provide less security. Users might have the best of both worlds if there was a good way of speedy movement between both communities.
To prepare for the broad adoption of Web 3.0, which will see an influx of over a billion users, we must be prepared to embrace a multichain strategy, which will eliminate cumbersome transactions and provide end-users with a frictionless experience.
Multichain blockchain has updated the blockchain technology for use by enterprises with distinct features such as scalability, a faster transaction speed, and the facility of interconnected blockchains. These features make multichain blockchain apt for financial transactions, and it is being adopted by banks and financial institutions. So if you are looking for a seamless blockchain experience that can be deployed by enterprises at a higher transaction speed and start your journey on Multichain.
Get ready to refine your app development concepts by reaching out to Appventurez, a trusted and reliable blockchain app development company. As a firm specializing in blockchain app development services, we are well-equipped to support you in advancing your decentralized journey.
Q. What is multi-chain technology and what are the objectives?
MultiChain technology is a platform that allows users to create private Blockchains that may be used for financial transactions by businesses. MultiChain gives us a straightforward API and command-line interface. This aids in the preservation and establishment of the chain.
Q. Is Multichain open source?
MultiChain is an open-source platform for private blockchains that includes significant configurability, quick deployment, permissions management, native assets, and data streams, among other things.
Q. What is a multi-chain?
Multi-chain is a technique that needs projects to exist simultaneously on at least two blockchains. This makes it easier to communicate between different blockchains. Polkadot and Cosmos are two multi-chain initiatives.


Elevate your journey and empower your choices with our insightful guidance.

VP – Pre Sales at Appventurez
Anand specializes in sales and business development as its VP - Sales and Presales. He supervises the pre-sales process by upscaling on establishing client relationships. He skillfully deploys instruments such as cloud computing, automation, data centers, information storage, and analytics to evaluate clients’ business activities.
You’re just one step away from turning your idea into a global product.
Everything begins with a simple conversation.