Over the past few years, whether you’ve been closely following developments in banking, investing, or the world of cryptocurrencies, you’ve likely encountered the term “Blockchain Technology.” It might have even been introduced to you primarily as “Cryptocurrency,” a term that has gained immense popularity in recent times. To grasp the fundamentals of blockchain, it’s essential […]
Updated 30 January 2024

VP – Pre Sales at Appventurez
Over the past few years, whether you’ve been closely following developments in banking, investing, or the world of cryptocurrencies, you’ve likely encountered the term “Blockchain Technology.” It might have even been introduced to you primarily as “Cryptocurrency,” a term that has gained immense popularity in recent times. To grasp the fundamentals of blockchain, it’s essential to start with a clear definition.
Blockchain app development services involve the creation of a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger system, safeguarded through cryptography. At its core, it functions as a continually evolving and well-organized record-keeping mechanism. Despite the intricate nature of the concept, grasping blockchain is simpler than it appears. In essence, a blockchain development company manages a chronological sequence of immutable data records through a network of computers, ensuring that no single entity maintains control. These blocks of information are securely interconnected using cryptographic principles.
Now, what makes Blockchain app development Services truly remarkable? Why do we assert that it has the potential to disrupt entire industries? How does this transformative technology operate?
A blockchain system is a simple chain of information containers. Each block has a cryptographic hash of the previous information block, timestamp, and transaction history. The whole schema is really simple and secure making Blockchain immune to data tampering.
Blockchain technology is a peer-to-peer open distributed transaction process that can construct transactions between two parties securely and efficiently. Blockchain technology is secure and not susceptible to hacking because, once recorded, the data in any block can’t be updated retroactively without changing all subsequent blocks.
According to the blockchain basics, Blockchain is sort of like Facebook News Feed which gives a live update to its users whenever a new status is posted. Similarly, the blockchain network works in the same manner. Anyone can view the data in it but when a user tries to connect their portable computers to the blockchain network, the computer automatically receives a copy of the blockchain and updates when the new block is added.
In the blockchain hierarchy, there are millions of copies of the same blockchain but everyone is unique. There is not a single account of events that can’t be managed with blockchain, and a hacker would need to manipulate every copy of the blockchain on that particular network. In the blockchain system transactions are not fully anonymous. Their data is restricted to their digital signature or username.
In a blockchain system, when a block is added at the end of the row, it’s really difficult to go back and put some alternative data into the block after erasing the original content. Each block assigns its hash and every hash is created by a math function driven by an algorithm that molds the digital info into some letter and number containing a string. A hacker needs an immense and improbable amount of computing power to replace the content of every block.
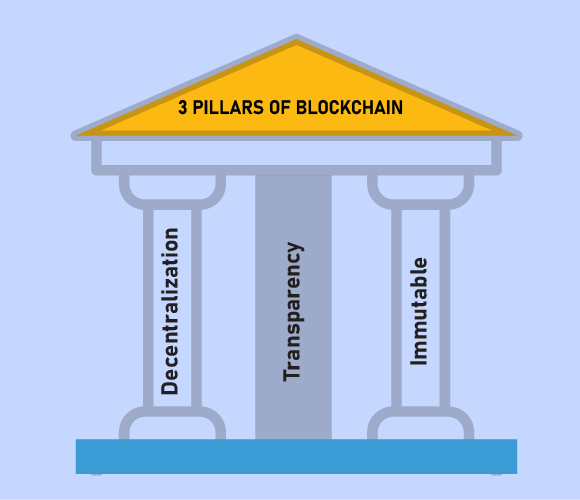
The three main sections of Blockchain Technology and blockchain basics which have assisted it to gain extensive recognition are as follows:
Decentralization is the most prominent characteristic of Blockchain. Being a P2P gateway, no single institution can command the blockchain network. It’s just maintained by a group of coders, run by an open network of dedicated computers scattered around the world.
Transparency in blockchain signifies every single transaction is public with an open view. As a blockchain explorer with a public user address, it’s feasible to view it. Earlier, the financial institutions were able to use the consumers’ funds but at this point, blockchain doesn’t sustain that. Blockchain is a classified database that can transparently record every digital transaction.
The most frequent word that we apprehend about the blockchain is permanent and the whole operation of the blockchain system is designed to be perpetual means durable. Blockchain is a one-directional process and never changes where a piece of data can enter.
In the blockchain database, a list of sequential data is called a block that is continuously storable and refillable. The trusted nature of blockchain is legitimate and also validated by multiple participants.
The marvel of Blockchain technology lies in its ability to grant individuals new ownership rights through digital relationships. This aspect becomes particularly intriguing as blockchain solutions offer a unique opportunity to craft a potent digital identity. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that ownership is securely established and verified, ushering in a new era of digital empowerment. As businesses and individuals explore the possibilities of blockchain, the demand for tailored solutions is on the rise, underscoring the significance of blockchain app development services in creating robust and personalized applications that leverage the transformative potential of this technology.
A unique physical item authentication, paired with a digital token. The main aim of the token is to convert physical data into digital data. For supply chain management, the Digi tokens are very useful for fraud detection and anti-counterfeiting.
Blockchain technology represents an evolution of how digital information is collected and gathered. It means according to the blockchain basics, it’s less about maintaining a database and more about managing the system record.
Blockchain uses the client-server infrastructure and offers to create a record automatically, set the rights for who has access to information, and, give the controls on permissions required to view the info.
Blockchain is a cryptographically secure, regular updates and a distributed ledger that allows transferring data securely. Using blockchain, IoT enables the secure option and trustful messaging between different IoT devices through IoT networks. When IoT devices collaborate with blockchain, smart devices become feasible to exchange data and initiate financial transactions through a decentralized blockchain.
The hottest buzzword of this year among stock marketers and investors is blockchain technology and blockchain basics. In stock trading, the added efficiency in share settlement makes an organized and efficient process when peer-to-peer trade confirmations as opposed to taking three days for clearance.
With well-known companies like Uber and Airbnb flourishing, the sharing economy has already proven successful. The collaboration of blockchain and shared economy while enabling peer-to-peer payments, blockchain makes a truly decentralized cooperative economy results.
With a high degree of accuracy, blockchain proves the crowdsourcing of predictions on probability. Prediction marketers can earn money by buying the appropriate prediction. The “wisdom of the crowd” technology will be fully accurate in the upcoming years and that will maybe be the higher payout for the marketers.
Now we are going to discuss the most attractive and innovative portion of blockchain technology as well as an evolution of the finance application development industry, which has changed the definition of secure fund transfer.

Cryptocurrency is an innovative, open-source, and Person-to-person (P2P) payment network like conventional dollars, euros, or yen, and a new kind of money was introduced by a pseudonymous software developer Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. It is an electronic payment system based on mathematical proof, that was produced for exchange, independent of any central authority, that could be transferred electronically in a secure, verifiable, and stable way. This makes users wonder what are unique benefits of the structure of a block are.
Let us give you an inside on the benefits of digital currencies:
Limited supply is another feature that makes Cryptocurrency more engaging as an asset. Fiat currencies like dollars, euros, yen, etc. have an inexhaustible supply. Central banks can distribute digital currencies as much as they want. But in the case of Cryptocurrency, the supply is regulated by the underlying algorithm. Limited supply is a theory applied to Cryptocurrency – if the demand is high and supply is constant, the value will increase.
Users of Cryptocurrency, in theory, operate in semi-anonymity. When a transaction application is submitted, the protocol checks all previous transactions to confirm that the sender has the necessary cryptocurrency, as well as the authority to send them. The system does not need to know any user identity. The network is distinct, and the progress of a particular transaction is visible to all. It proves that Cryptocurrency is not an ideal currency for criminals, terrorists, or money launderers.
This is because there is no central “adjudicator” that can say “ok, return the money.” If a transaction is registered on the network, and if more than an hour has passed, it is impossible to modify. It means that any transaction on the crypto network cannot be tampered with.
Most blockchains are designed as a decentralized database that functions as distributed digital entries. This blockchain records and stocks data in blocks, which are organized in a chronological sequence and are linked through cryptographic proofs. The production of blockchain technology brought up many benefits in a variety of enterprises, rendering developed protection in trustless circumstances. However, its decentralized constitution also brings some disadvantages. For instance, when compared to traditional centralized databases, blockchains present limited capability and require progressed storage potential.
Let us see some of the major Blockchain advantages and disadvantages.
Since blockchain data is often saved in thousands of devices on a distributed network of nodes, the method and the data are extremely repellent to technical malfunctions and wicked intrusions. Each network connection can replicate and store a copy of the database and, because of this, there is no single point of bankruptcy. A single node going offline does not affect the availability or safety of the network.
In distinction, many conservative databases rely on a single or a few servers and are more defenseless to technical malfunctions and cyber-attacks.
Fortified blocks are extraordinary to be converted, meaning that once data has been designated into the blockchain, it is remarkably difficult to remove or change it. This makes blockchain a great technology for collecting financial records or any other data where an audit trail is required because every change is shadowed and enduringly registered on dispersed and public entries.
In most common payment methods, transactions are not only reliant on the two parties concerned, but also on an intermediary – such as a bank, credit card association, or payment provider. When using blockchain technology, this is no longer needed because the distributed network of nodes verifies the transactions through a method known as mining. For this reason, Blockchain is usually referred to as ‘trustless’ conformity.
The Record of Work agreement algorithm that protects the Bitcoin blockchain has been demonstrated to be very effective over the years. However, there are a few possible interventions that can be performed on blockchain networks and 51% of attacks are among the most contested. Such an intervention may happen if one entity accomplishes control of more than 50% of the network hashing power, which would ultimately cause them to confuse the network by deliberately dismissing or restricting the systemization of transactions.
Another downside of blockchain operations is that once data has been appended to the blockchain it is extremely challenging to mitigate it. While efficiency is one of blockchain’s benefits, it is not always satisfying. Changing blockchain data or code is usually very troublesome and often requires an inebriating fork, where one chain is dropped, and a new one is seized up.
Blockchains, particularly those using Proof of Work, are highly unproductive. Since mining is highly aggressive and there is just one champion every ten minutes, the work of every other miner is consumed. As miners are continuously trying to increase their computational endowment, so they have a greater chance of finding a valid block confusion. The supplies used by the Bitcoin network have developed significantly in the last few years, and it currently consumes more energy than many countries, such as Denmark, Ireland, and Nigeria.


Elevate your journey and empower your choices with our insightful guidance.

VP – Pre Sales at Appventurez
Anand specializes in sales and business development as its VP - Sales and Presales. He supervises the pre-sales process by upscaling on establishing client relationships. He skillfully deploys instruments such as cloud computing, automation, data centers, information storage, and analytics to evaluate clients’ business activities.
You’re just one step away from turning your idea into a global product.
Everything begins with a simple conversation.